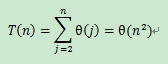Analysis of Algorithms(Study Notes Ⅰ)
算法分析是关于计算机程序性能和资源利用的理论研究。
If you want to be a good programmer, you just program every day for two years, you will be an excellent programmer.
If you want to be a world-class programmer, you can program every day for ten years, or you can program every day for two years and take an algorithms class.
-Charles Leiserson
下面以经典的排序问题进入这个话题:
Problem sorting
Input: sequence<a1 ,a2,…,an> of numbers
Output: permutation <a1’,a2’,…,an’>
$(such that): a1’≤a2’≤…≤an’
Insertion sort
以下为伪代码(pseudocode):Insertion Sort(A1…n) // Sorts A[1,…,n] for j←2 to n do key ← A[j] i ← i-1 while i>0 and A[i] > key do A[i+1] ← A[i] i ← i-1 A[i+1] ← key
Java代码实现可参照《Java人肉实现数组排序》
下面分析插入排序的时间复杂度:
Runnning time
Depends on input(e.g. already sorted)
Depends on input size(6 elements vs 6*109)
parameterize things input size
want upper bonds
guarantee to user
插入排序的算法运行时间主要取决于要进行排序的序列的规模与是否有序。我们之所以关注它运行所要花费的时间上限是为了给用户一个承诺,所以讨论最小运行时间没有意义(目前)。
Kinds of analysis
- Worst-case analysis (usually)
T(n) = maximun time on any input of size n.
- Average-case analysis (sometimes)
T(n) = expected time over all inputs of size n.
(Need assumption of the statistical distribution of inputs)
- Best-case analysis (bogus)
Cheat with a slow algorithm : take any slow algorithm that you want and just check for some particular input.
对于Average-case,我们需要建立一个关于输入序列的统计分布的假设,然后通过求取它的加权平均数得到T(n)。
再一次说明为什么不讨论最小运行时间:因为一些时间复杂度较不理想的算法有时在特定的序列下表现得很好。
What is insertion sort’s worst-case time ?
Depends on computer
relative speed (on some machine)
absolute speed (on different machines)
Big IDEA of Algorithm – Asympthotic analysis (渐近分析)
Ignore machine-dependent constants instead of the actual running time.
Look at growth of the running time (T(n) as n → ∞).
Asymptotic notation (渐近符号)
θ-notation (theta) :
Drop low order terms
Ignore leading constants
两个要点:舍去低阶项;忽略前导常数。
Ex: 3n3 + 90n2 –5n + 6046 = θ(n3)
As n → ∞ , θ(n2) algorithm always be as a θ(n3) algorithm.
Insertion sort analysis
Worse-case: input reverse sorted.
(j times some constants)
Is insertion sort fast?
Moderately fast , for small n.
Not at all for large n.
to be continued…